Tibial Thrust Vs Cranial Drawer
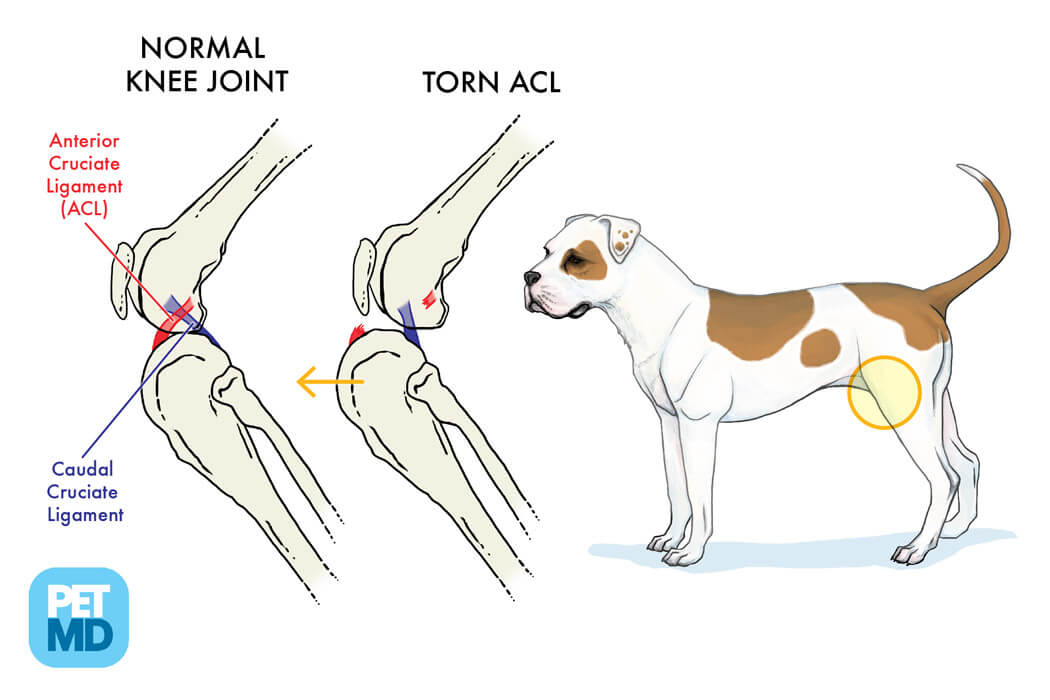
Tibial Thrust Vs Cranial Drawer - Another sign referred to as tibial thrust, may be elicited as well. Web the tibial thrust test and the cranial drawer test are the two main tests for instability in the knee. In this case the cranial cruciate ligament is ruptured, resulting in movement (cranial translation). Cranial cruciate ligament (crcl) rupture is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in dogs. Sliding of the distal femur over the proximal tibia
Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Web physical and radiographic examination techniques are commonly used to diagnose crcl deficiency. This systematic review aims to investigate whether one technique is superior to the other. This stifle is normal, and thus the tests are negative. Clinical signs clinical signs are different in intensity according to the degree and duration of crcl partial rupture. When cranial tibial thrust exceeds the tensile strength of a healthy cranial cruciate ligament or a weakened, degenerative cranial cruciate ligament, the ligament completely or partially. Web in these dogs the cranial tibial thrust caused by the forces acting on the slope of the tibial plateau continuously stresses the crcl and causes its partial rupture progressing with time in complete rupture.
Drawer Test Bruin Blog
This systematic review aims to investigate whether one technique is superior to the other. For the tibial thrust test, the dog often stands (it is less stressful) and your veterinarian will hold the femur (thigh bone) stable while bending the foot. It is performed by applying a force to the tibia while holding the femur.
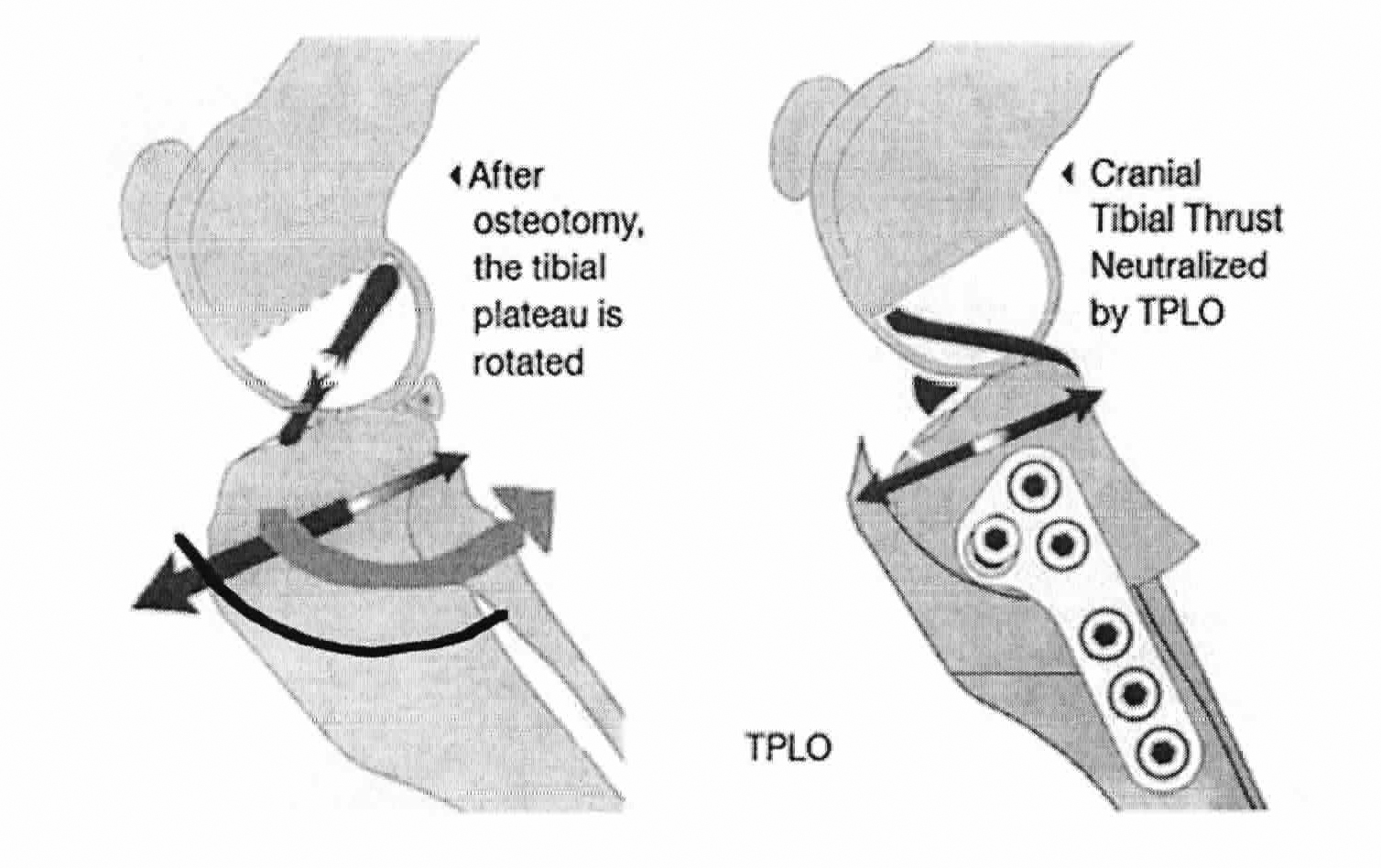
Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy
Web tibial plateau leveling osteotomy (tplo) or tibial tuberosity advancement (tta) are commonly used surgical techniques for correction of cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) rupture in dogs. Web the magnitude of the cranial tibial thrust is a function of external ground reaction forces, internal muscular forces, and the slope of the tibial plateau. Unstable partial tears.
Bones of the Lower Limb Anatomy and Physiology I
Weight bearing creates a force that pushes the femur down the slope of the tibia. Web increasing tibial loads in the tibial plateau leveled crcl deficient stifle increased caudal tibial thrust.(6) the cranial drawer sign may still be present after tplo surgery. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or.
Tibia alignment Varus (1a), normal (1b), and varus (1c) knee. Red
Web even with 25 years of experience as a veterinary orthopedic surgeon, i would estimate that examination with the cranial drawer sign or tibial thrust allows me to diagnose crclr in only about 80% of the dogs that subsequently undergo surgery, even though virtually 100% of these dogs have visible cruciate damage at arthrotomy. Web.
PPT Knee Orthopaedic Tests PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Web in these dogs the cranial tibial thrust caused by the forces acting on the slope of the tibial plateau continuously stresses the crcl and causes its partial rupture progressing with time in complete rupture. Your pet’s doctor will take the results from the drawer sign test into consideration when determining a treatment plan for.
ACL and CCL diagram provided by PetMD
At this time, there was absent cranial drawer and tibial thrust with marked periarticular fibrosis of the stifle. Seven months later, the dog was reexamined, and arthroscopy was performed on the contralateral stifle. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. The ccl has 3 main functions: The advancement.
Representative scheme of forces acting on stifle joint before (A) and
Cranial cruciate ligament (crcl) rupture is the most common cause of hindlimb lameness in dogs. The ccl has 3 main functions: Web the tibial thrust test and the cranial drawer test are the two main tests for instability in the knee. Web this video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression tests..
A most cranial point of the tibial plateau B most caudal point of the
For the tibial thrust test, the dog often stands (it is less stressful) and your veterinarian will hold the femur (thigh bone) stable while bending the foot. Web once the ligament tears to a certain degree the tibia can be manually manipulated to show instability in what is called the “cranial drawer test” in which.
Anatomical landmarks and corresponding reference systems. LE Lateral
Unstable partial tears have more instability than a stable partial tear and typically have instability equal to or less than dogs with a. According to slocum, a certain amount of drawer sign is built into the procedure to protect the integrity of the caudal cruciate ligament. The cranial drawer test is performed most commonly and.
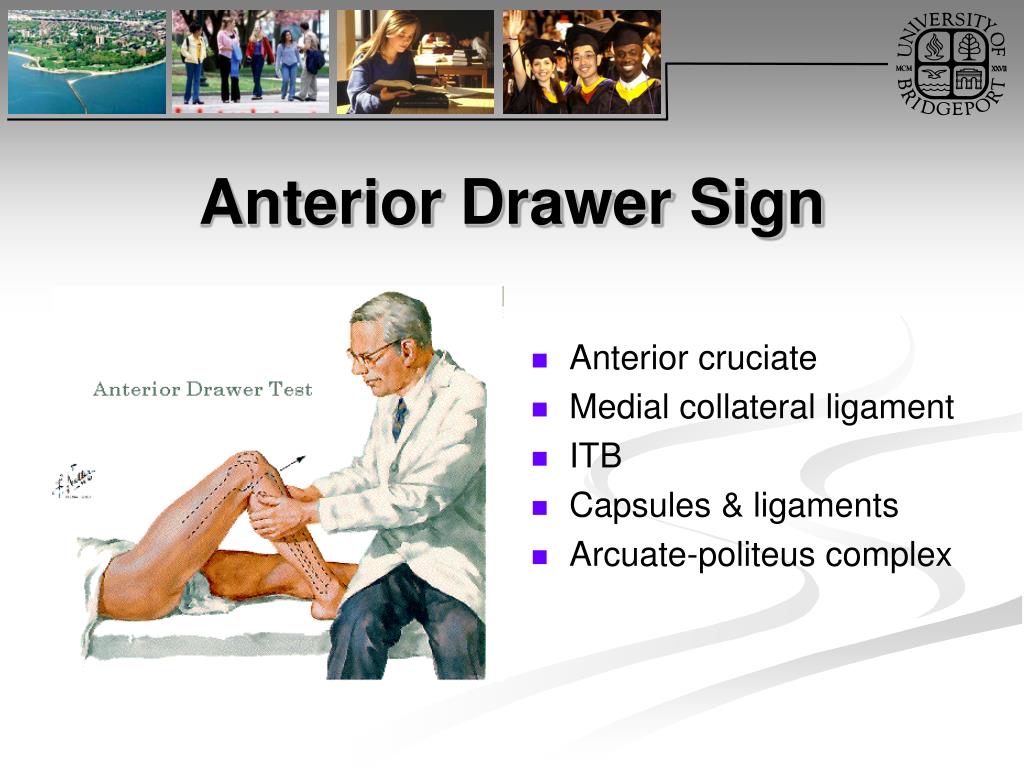
Anterior Drawer Test for ACL How to Perform the Anterior Drawer Test
In this case the cranial cruciate ligament is ruptured, resulting in movement (cranial translation). It is performed by applying a force to the tibia while holding the femur stable, thereby. Clinical signs clinical signs are different in intensity according to the degree and duration of crcl partial rupture. The cranial drawer assessment is best done.
Tibial Thrust Vs Cranial Drawer Web instability of the stifle is commonly demonstrated through the cranial drawer test and tibial compression test. Web tibial plateau leveling osteotomy (tplo) or tibial tuberosity advancement (tta) are commonly used surgical techniques for correction of cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) rupture in dogs. Web in these dogs the cranial tibial thrust caused by the forces acting on the slope of the tibial plateau continuously stresses the crcl and causes its partial rupture progressing with time in complete rupture. Seven months later, the dog was reexamined, and arthroscopy was performed on the contralateral stifle. The ccl has 3 main functions:
Web The Tibial Thrust Test And The Cranial Drawer Test Are The Two Main Tests For Instability In The Knee.
Web once the ligament tears to a certain degree the tibia can be manually manipulated to show instability in what is called the “cranial drawer test” in which the tibia can be moved forward in relation to the femur. Web tibial plateau leveling osteotomy (tplo) or tibial tuberosity advancement (tta) are commonly used surgical techniques for correction of cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) rupture in dogs. Web tibia (tibial plateau) is sloped. This stifle is normal, and thus the tests are negative.
This Force Is Called “Tibial Thrust” And The Job Of The Ccl Is To Prevent This Motion.
Web instability of the stifle is commonly demonstrated through the cranial drawer test and tibial compression test. Web this video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression tests. Web cranial drawer and tibial thrust were present in both pelvic limbs. When cranial tibial thrust exceeds the tensile strength of a healthy cranial cruciate ligament or a weakened, degenerative cranial cruciate ligament, the ligament completely or partially.
Clinical Detection Of Tibial Translation By Cranial Drawer Test And Tibial Compression Test Can Aid Revealing Stifle Joint Instability As A Result Of Crcl Injury.
The cranial drawer test is performed most commonly and tends to be the mainstay of testing for stifle instability by general veterinarians. Web the magnitude of the cranial tibial thrust is a function of external ground reaction forces, internal muscular forces, and the slope of the tibial plateau. Web a stable partial tear has cranial drawer and cranial tibial thrust that is similar to or slightly increased compared to a normal dog stifle. Sliding of the distal femur over the proximal tibia
Another Sign Referred To As Tibial Thrust, May Be Elicited As Well.
For the tibial thrust test, the dog often stands (it is less stressful) and your veterinarian will hold the femur (thigh bone) stable while bending the foot. Web this video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression (tibial thrust) tests. Web in these dogs the cranial tibial thrust caused by the forces acting on the slope of the tibial plateau continuously stresses the crcl and causes its partial rupture progressing with time in complete rupture. Clinical signs clinical signs are different in intensity according to the degree and duration of crcl partial rupture.