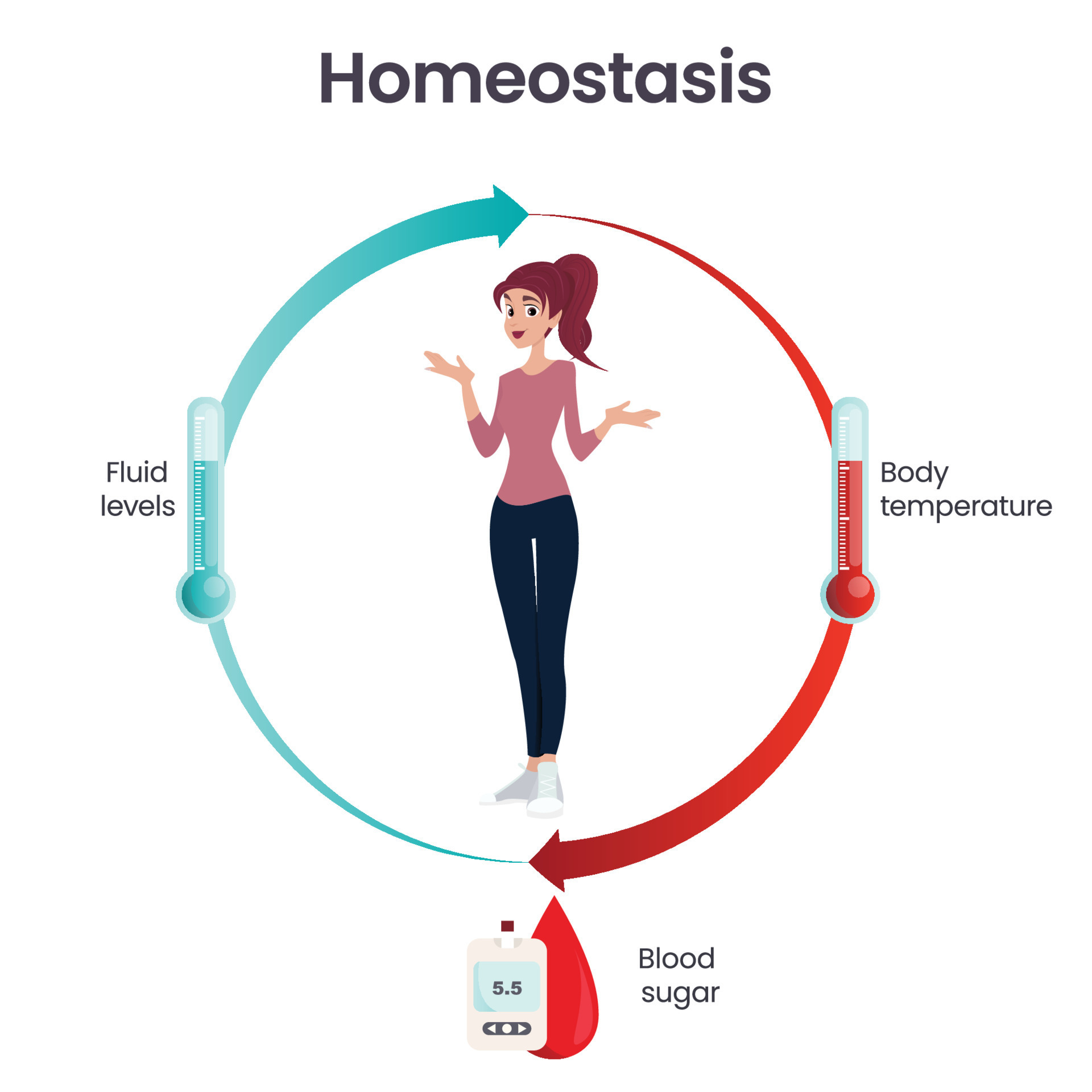
Homeostasis Drawing
Homeostasis Drawing - It also covers examples of different systems involved in maintaining. Web download a pdf of the lab to print. Web your body regulates other chemical mechanisms as well to keep systems in balance. Homeostasis is an organism’s process of maintaining a stable internal environment suitable for sustaining life. Stasis = “standing still”) means to maintain body functions within specific livable ranges, adjusting.
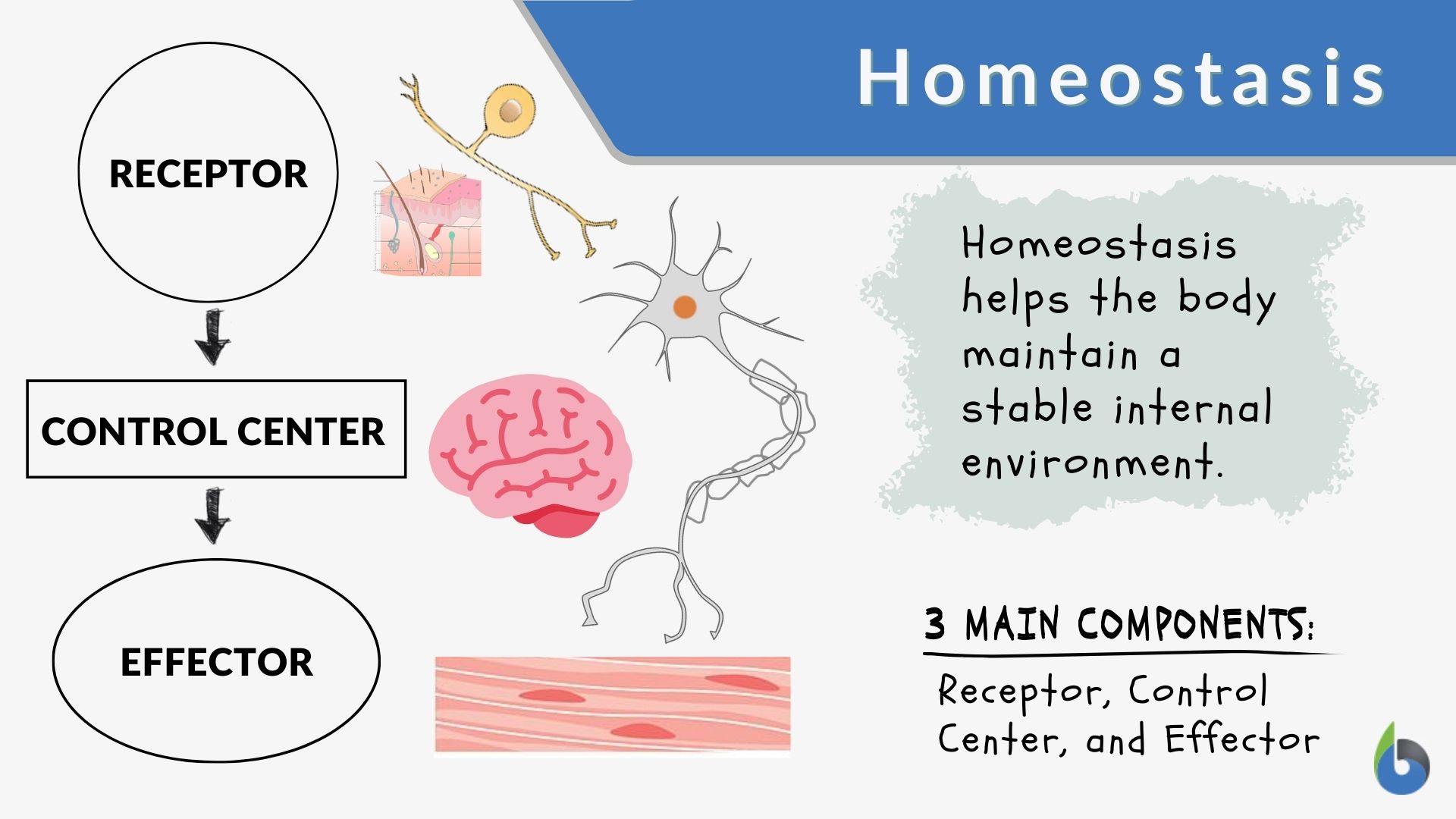
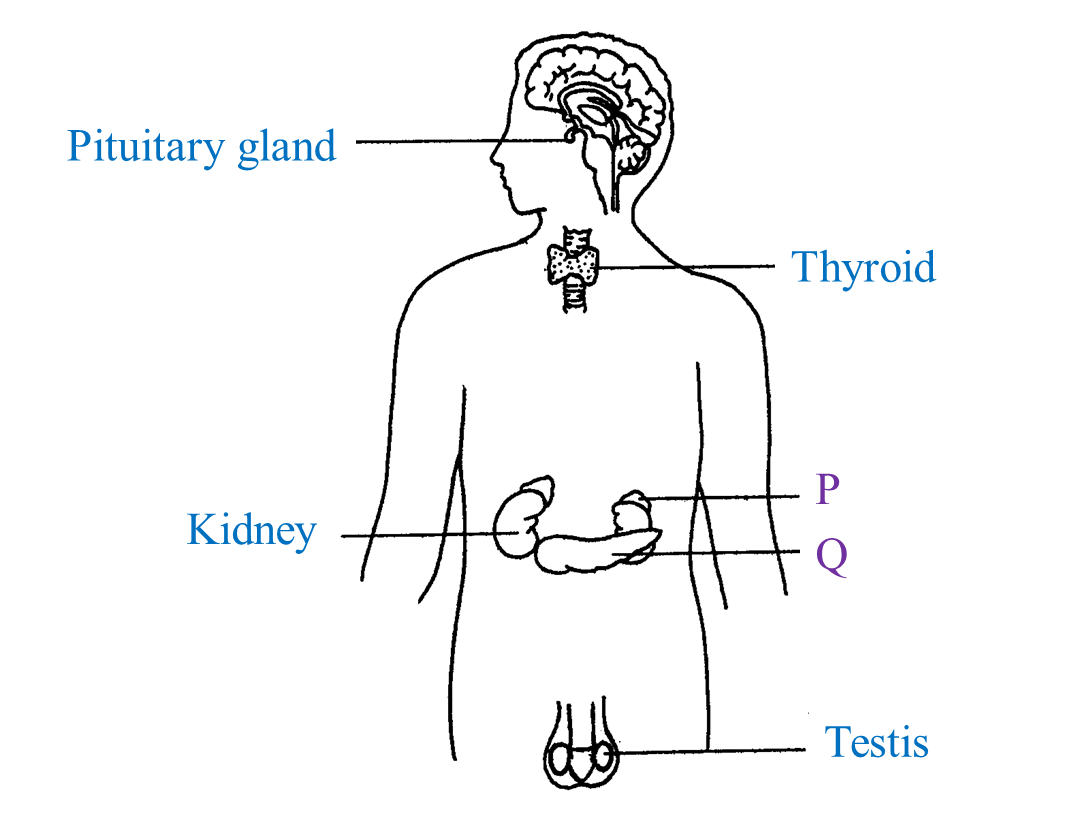
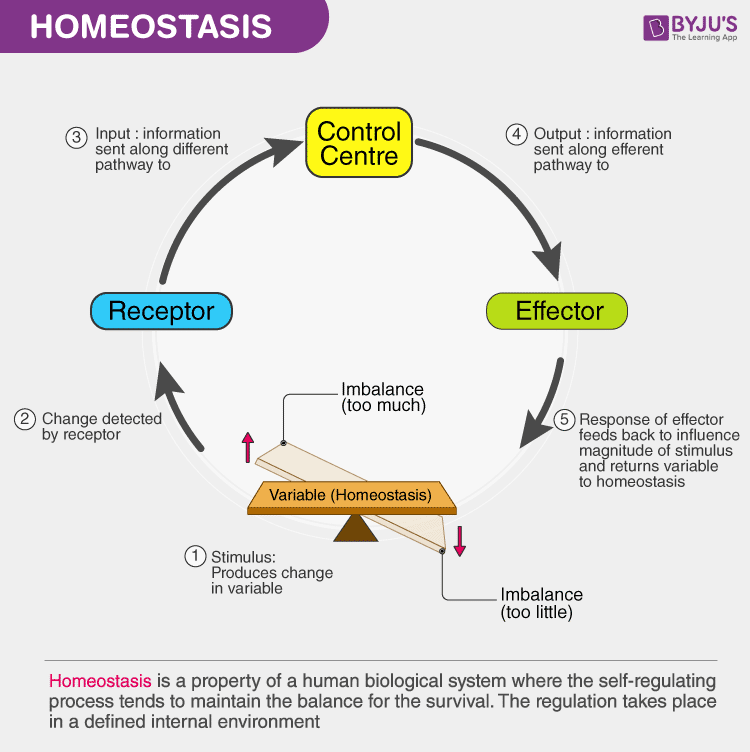
Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. These use hormones as chemical signals—for example, in the case of blood. Web all cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. This article explains what homeostasis is and how it works in organisms to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions through negative feedback loops and positive feedback loops. Identify and define the four interacting components that maintain homeostasis in. Physiologically, it is the body’s attempt to maintain a constant and balanced. Learn about homeostasis in humans,.
Homeostasis Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
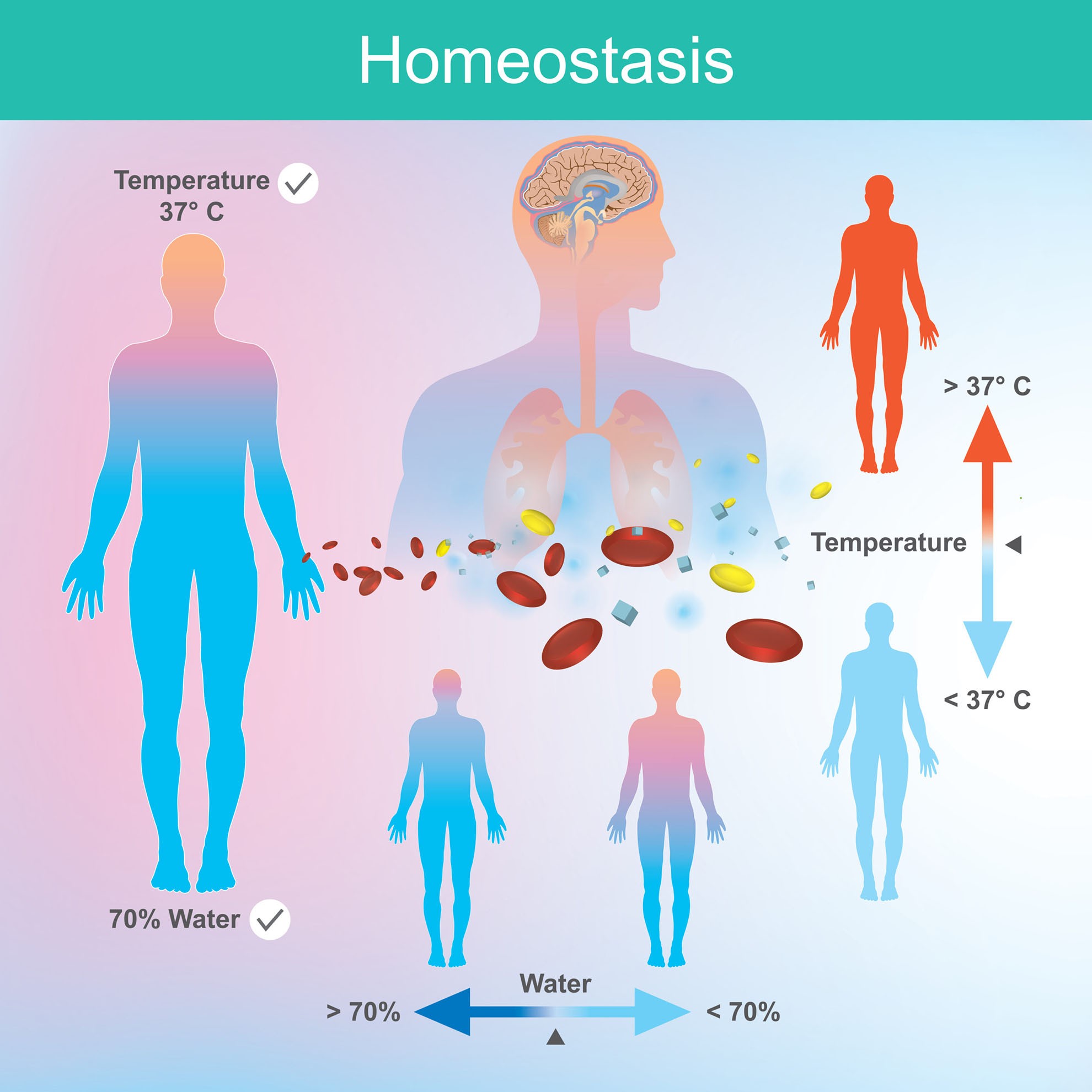
Homeostasis describes the dynamic balance of the body’s internal environment and the effort to maintain a constant, stable inside. Stasis = “standing still”) means to maintain body functions within specific livable ranges, adjusting. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain. Within these loops, negative stimuli automatically trigger mechanisms to help. Identify and.
13.7.1 Homeostasis in Human (Structured Question 1 & 2) SPM Biology
Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. There are many body components that contribute to homeostasis. Web learn how your body maintains proper homeostasis and regulates temperature, blood pressure, blood ph and blood sugar. Homeostasis, in a general sense, refers to stability, balance, or equilibrium. It is essentially a corrective mechanism, consider.
Physiological Homeostasis Biology Online Tutorial
Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis; Stasis = “standing still”) means to maintain body functions within specific livable ranges, adjusting. (b) body temperature is regulated by negative feedback. Within these loops, negative stimuli automatically trigger mechanisms to help. These use hormones as chemical signals—for example, in the case of blood. Web this.
Best Describes the Process of Homeostasis
Homeostasis, in a general sense, refers to stability, balance, or equilibrium. Web your body regulates other chemical mechanisms as well to keep systems in balance. It also covers examples of different systems involved in maintaining. Physiologically, it is the body’s attempt to maintain a constant and balanced. Web this occurrence is known as physiological homeostasis,.
Teoria de la Homeostasis, Biologia I, UNIDAD I.
Homeostasis is an organism’s process of maintaining a stable internal environment suitable for sustaining life. Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis; It also covers examples of different systems involved in maintaining. Learn about homeostasis in humans,. Within these loops, negative stimuli automatically trigger mechanisms to help. Web (a) a negative feedback loop.
Biology homeostasis science vector illustration infographic 20561283
In order to set the system in motion, a stimulus must drive a. This lab activity will focus on the liver and the kidneys. Web download a pdf of the lab to print. Web learn how your body maintains proper homeostasis and regulates temperature, blood pressure, blood ph and blood sugar. In biology, homeostasis (.
Homeostasis Biology I
In biology, homeostasis ( british also homoeostasis) (/hɒmɪə (ʊ)ˈsteɪsɪs/) is the state of steady internal, physical, chemical, and social conditions maintained by living systems. Stasis = “standing still”) means to maintain body functions within specific livable ranges, adjusting. Define the setpoint and normal range for physiological measures. This article explains what homeostasis is and how.
Homeostasis
Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. Identify and define the four interacting components that maintain homeostasis in. Homeostasis describes the dynamic balance of the body’s internal environment and the effort to maintain a constant, stable inside. Cells contain parts called organelles. Web about transcript homeostasis, or maintaining a steady body temperature,.
Maintaining homeostasis and listening to your body
(b) body temperature is regulated by negative feedback. This lab activity will focus on the liver and the kidneys. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. Describe thermoregulation of endothermic and ectothermic animals Web how it works homeostasis typically involves negative feedback loops. Learn about homeostasis in humans,. From body temperature to.
Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) Expii
Web how it works homeostasis typically involves negative feedback loops. Homeostasis describes the dynamic balance of the body’s internal environment and the effort to maintain a constant, stable inside. Web learn how your body maintains proper homeostasis and regulates temperature, blood pressure, blood ph and blood sugar. Learn about homeostasis in humans,. Describe thermoregulation of.
Homeostasis Drawing It also covers examples of different systems involved in maintaining. Web download a pdf of the lab to print. It is essentially a corrective mechanism, consider the following. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain. Web homeostasis is the activity of cells throughout the body to maintain the physiological state within a narrow range that is compatible with life.
Web Learn How Your Body Maintains Proper Homeostasis And Regulates Temperature, Blood Pressure, Blood Ph And Blood Sugar.
Define the setpoint and normal range for physiological measures. Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. Identify and define the four interacting components that maintain homeostasis in. Homeostasis describes the dynamic balance of the body’s internal environment and the effort to maintain a constant, stable inside.
Web Homeostasis Is The Activity Of Cells Throughout The Body To Maintain The Physiological State Within A Narrow Range That Is Compatible With Life.
Web all cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. Describe thermoregulation of endothermic and ectothermic animals Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis; Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.
(B) Body Temperature Is Regulated By Negative Feedback.
Web download a pdf of the lab to print. This lab activity will focus on the liver and the kidneys. Within these loops, negative stimuli automatically trigger mechanisms to help. Web your body regulates other chemical mechanisms as well to keep systems in balance.
Homeostasis, In A General Sense, Refers To Stability, Balance, Or Equilibrium.
Cells contain parts called organelles. There are many body components that contribute to homeostasis. Web how it works homeostasis typically involves negative feedback loops. Describe the factors affecting homeostasis ;