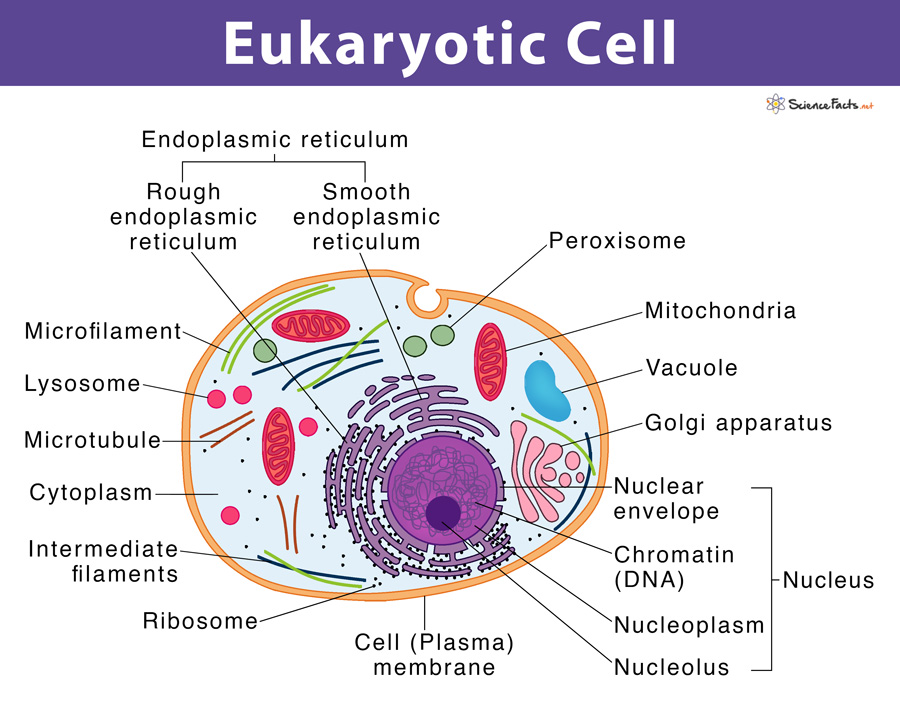
Drawing Of Eukaryotic Cell
Drawing Of Eukaryotic Cell - Web there are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Eukaryotic cells also contain other organelles besides the nucleus. Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria (cellular energy exchangers), a. Above all, eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence of a nucleus surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell’s nucleus, it has a “true.
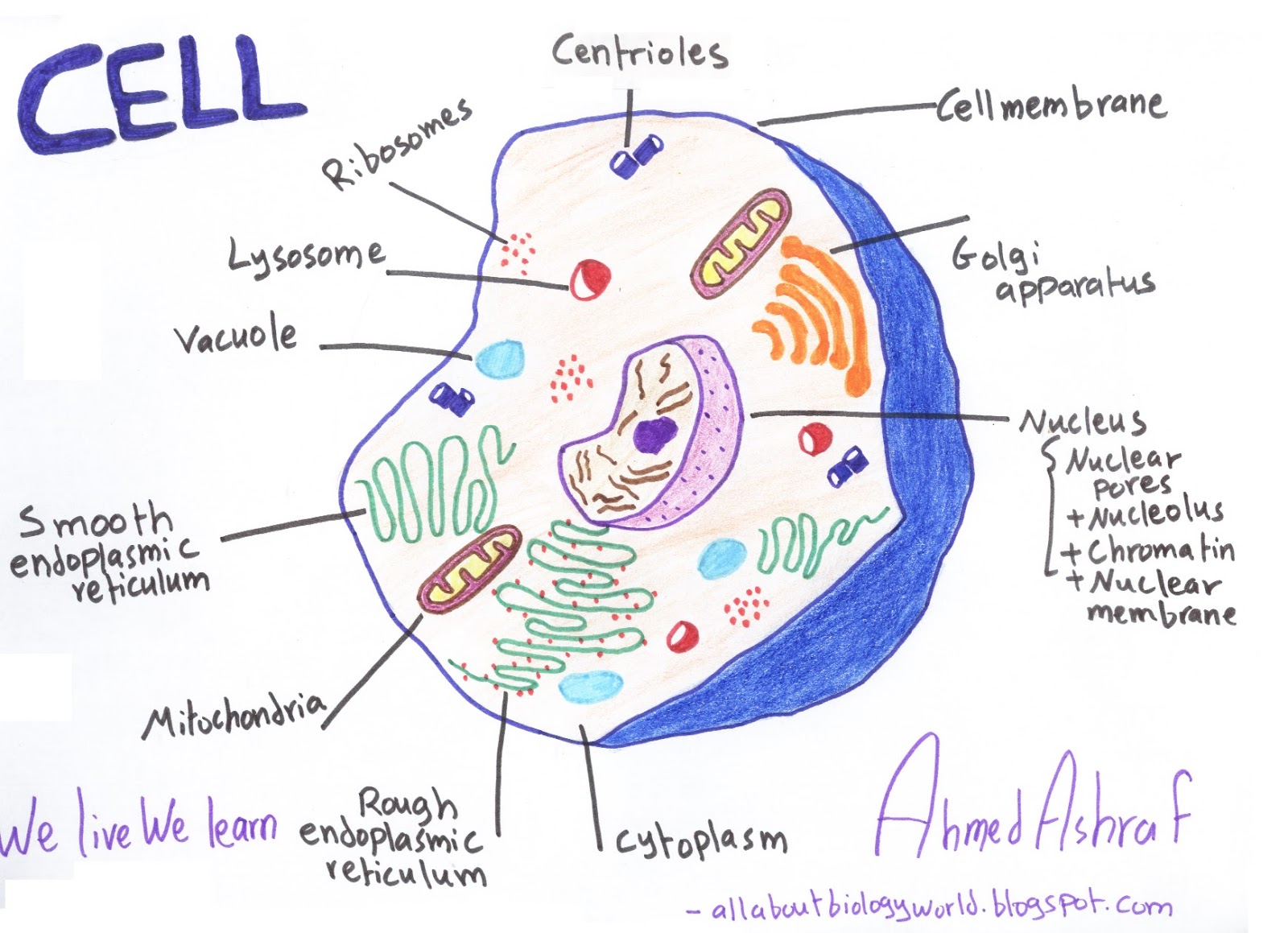
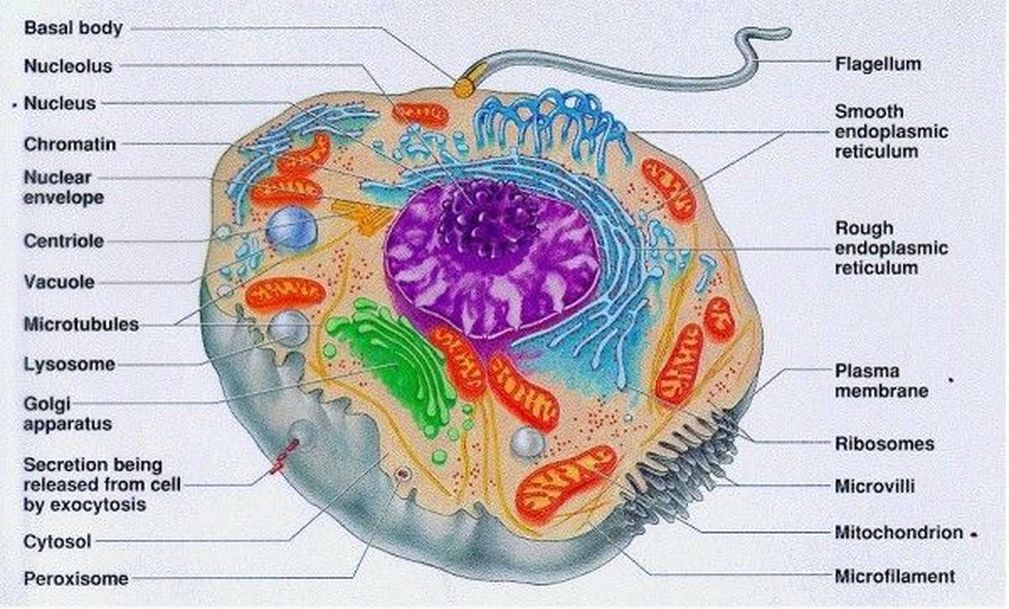
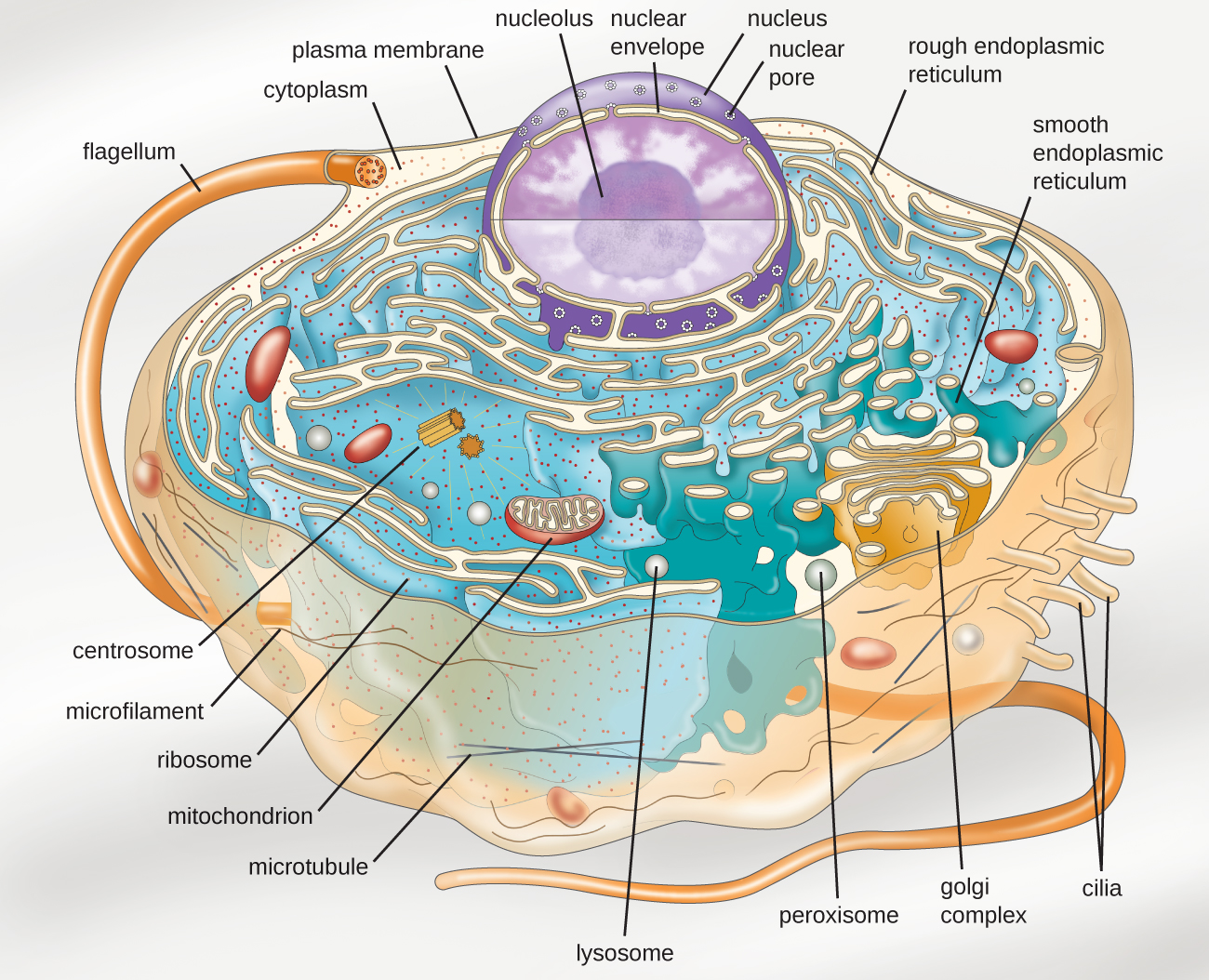
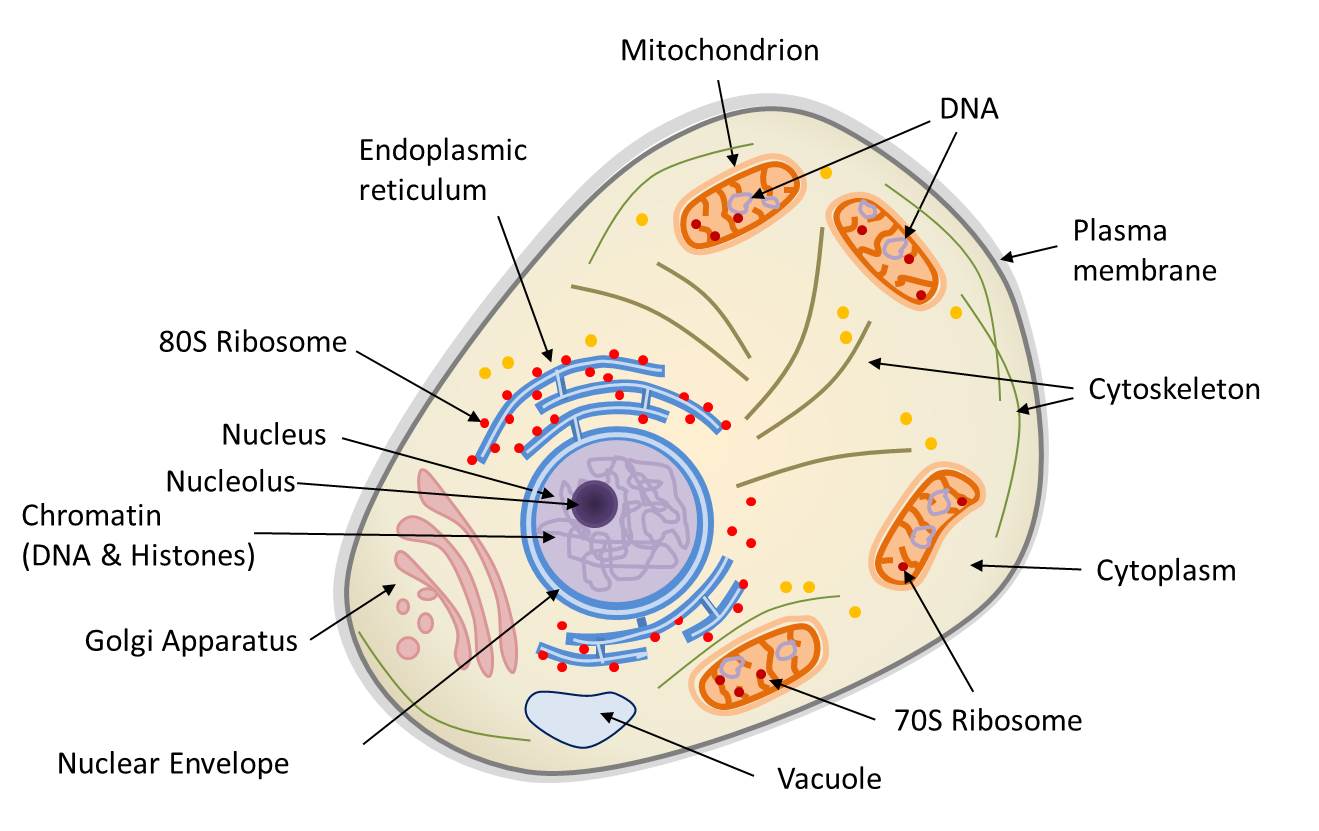
Cell wall is present in cells of plants, fungi and some protists. Web drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of each of the organelles. At this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. Web eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. Web 3d model the center for biomedical visualization at sgu 64.6k 95 triangles: State the role of the plasma membrane. Web eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell.
Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
Also identifying the difference between the plant and animal cell structure. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Web how to draw eukaryotic cell/ step by step drawing for beginners eukaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell diagram, step by step drawing for beginners, biology.
Biology Club Our cells 1 ( structure, function, division, disorder
The cytoskeleton is used to provide support and movement of the cell. It is absent in animal cells and some protists. The nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes are clearly mentioned in the diagram. A eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells. Above all, eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence.
Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
Makes up the cytoskeleton of the cell about 25 nm in diameter. A eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells. Web drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of each of the organelles. Web describe the structure of eukaryotic plant and animal cells. Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells, and.
2.4 Eukaryotic Cell Structure a level biology student
Organisms that are based on the eukaryotic cell are called “eukaryotes” and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria (cellular energy exchangers), a. Web 3d model the center for biomedical visualization at sgu 64.6k 95 triangles: Summarize the functions of the major cell organelles. Web eukaryote, any cell or.
Parts and functions of eukaryotic cell
Web describe the structure of eukaryotic plant and animal cells. Web eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. A eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells. Web we have come to understand that the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell is highly structured, permeated by rods and tubules. Web.
3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology 201
The cytoskeleton is used to provide support and movement of the cell. 2.3.2 annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure. Web drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of each of the organelles. Wall less cells are generally irregular. Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes, and they range from.
Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology
Web eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. Cell wall is present in cells of plants, fungi and some protists. Web the endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and.
Symbiosis and evolution at the origin of the eukaryotic cell
Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Web a typical eukaryotic cell is shown in figurebelow. Eukaryotic cells are usually larger than prokaryotic cells, and they are found mainly in multicellular organisms. State the role of the.
Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Structure, & Examples
The nucleus houses the cell’s dna and directs the synthesis of proteins and ribosomes. Made of α and β tubulin combined to form dimers, the dimers are then joined into protofilaments. Web the endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and connects the nuclear membrane.
Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
Web the endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and connects the nuclear membrane to the plasma membrane of a cell. Web the structure of the microtubule. Web describe the structure of eukaryotic plant and animal cells. Ribosomes and lyosomes and a number of tiny.
Drawing Of Eukaryotic Cell The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Web there are two general classes of cells that exist: Organisms with eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes, and they range from fungi to people. Web eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The three main components of this cytoskeleton are microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules.
The Rest Of Our Discussion Will Strictly Be On Eukaryotes.
Ribosomes and lyosomes and a number of tiny filament. Thirteen protofilaments in a cylinder make a microtubule. Web if you examine the diagram above depicting plant and animal cells, you will see in the diagram of a plant cell a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. A eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells.
Web The Cells Of Eukaryotic Organisms Have Several Distinguishing Characteristics.
Explore more about cell organelles Makes up the cytoskeleton of the cell about 25 nm in diameter. Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria (cellular energy exchangers), a. Cell wall is present in cells of plants, fungi and some protists.
State The Role Of The Plasma Membrane.
Wall less cells are generally irregular. Web unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell’s nucleus, it has a “true. The three main components of this cytoskeleton are microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules.
The Cytoskeleton Is Used To Provide Support And Movement Of The Cell.
Web eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells found in domains archaea and bacteria. Web there are two general classes of cells that exist: Web eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. The nucleus houses the cell’s dna and directs the synthesis of proteins and ribosomes.