Draw A Molecule Of Atp
Draw A Molecule Of Atp - Web interactive animation of the structure of atp adenosine triphosphate ( atp) is a nucleotide [2] that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and. Web 1 answer acquaintance nov 22, 2016 adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups. Web cells actually draw their energy from the phosphate tail of atp. Adenosine triphosphate (atp) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The structure of atp is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate.
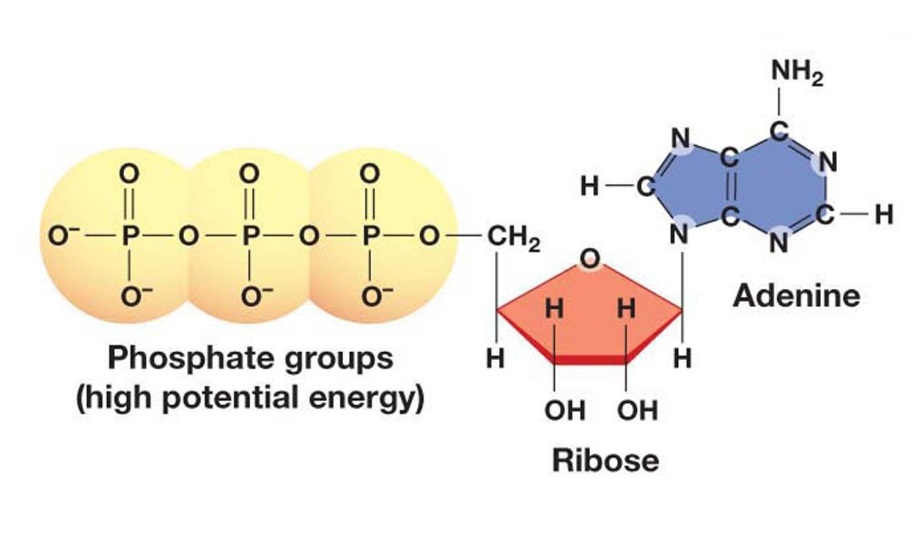
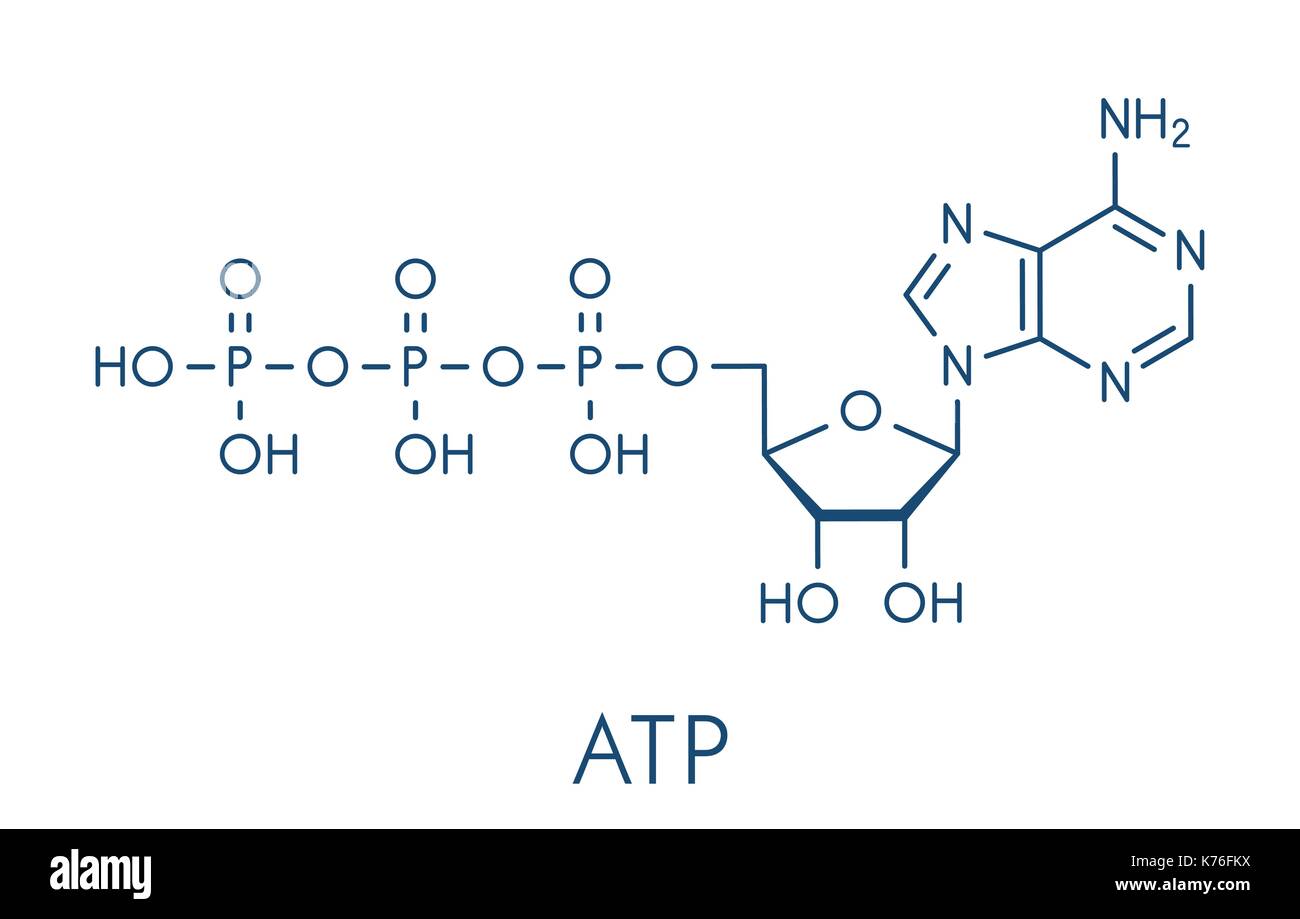
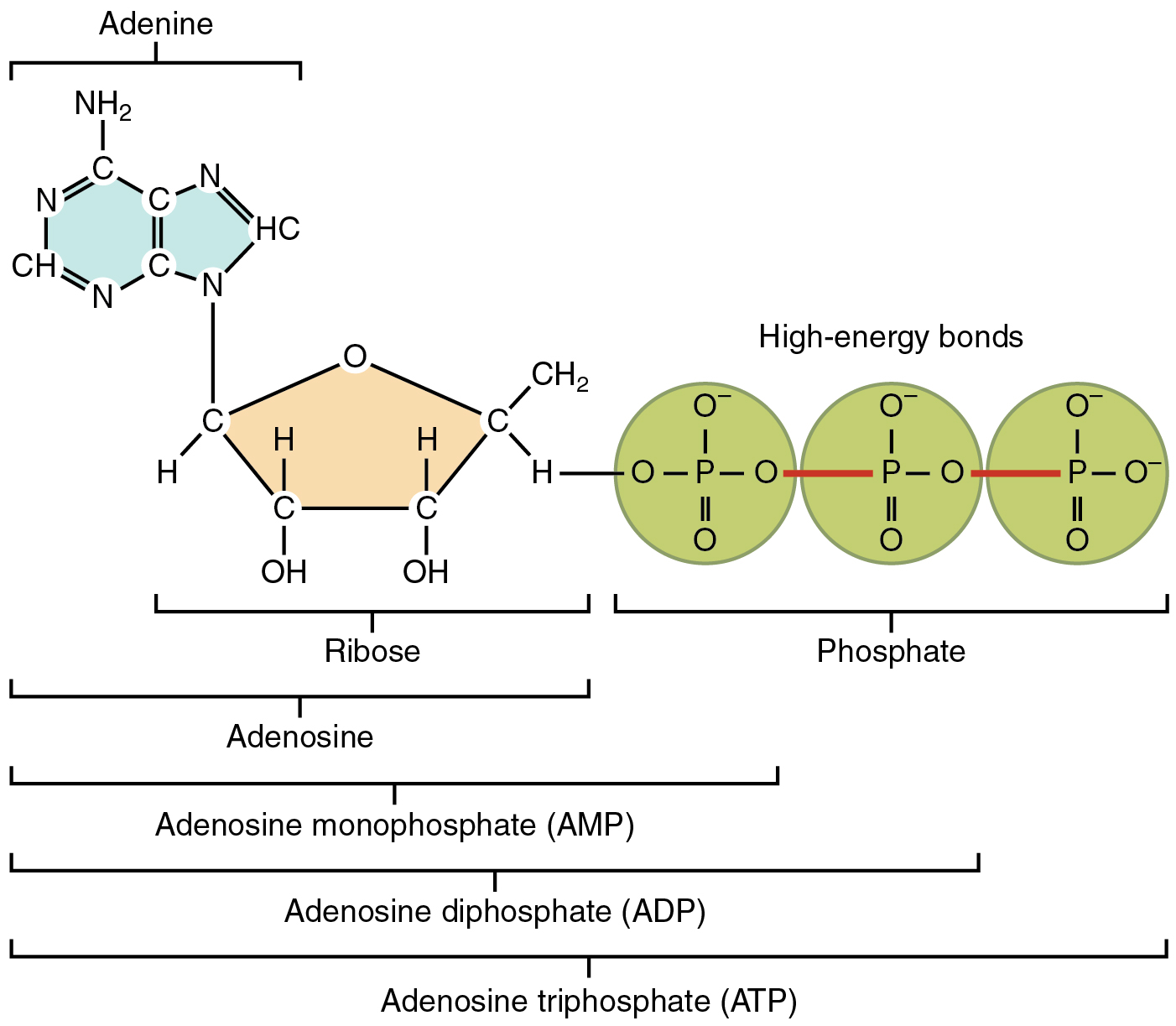
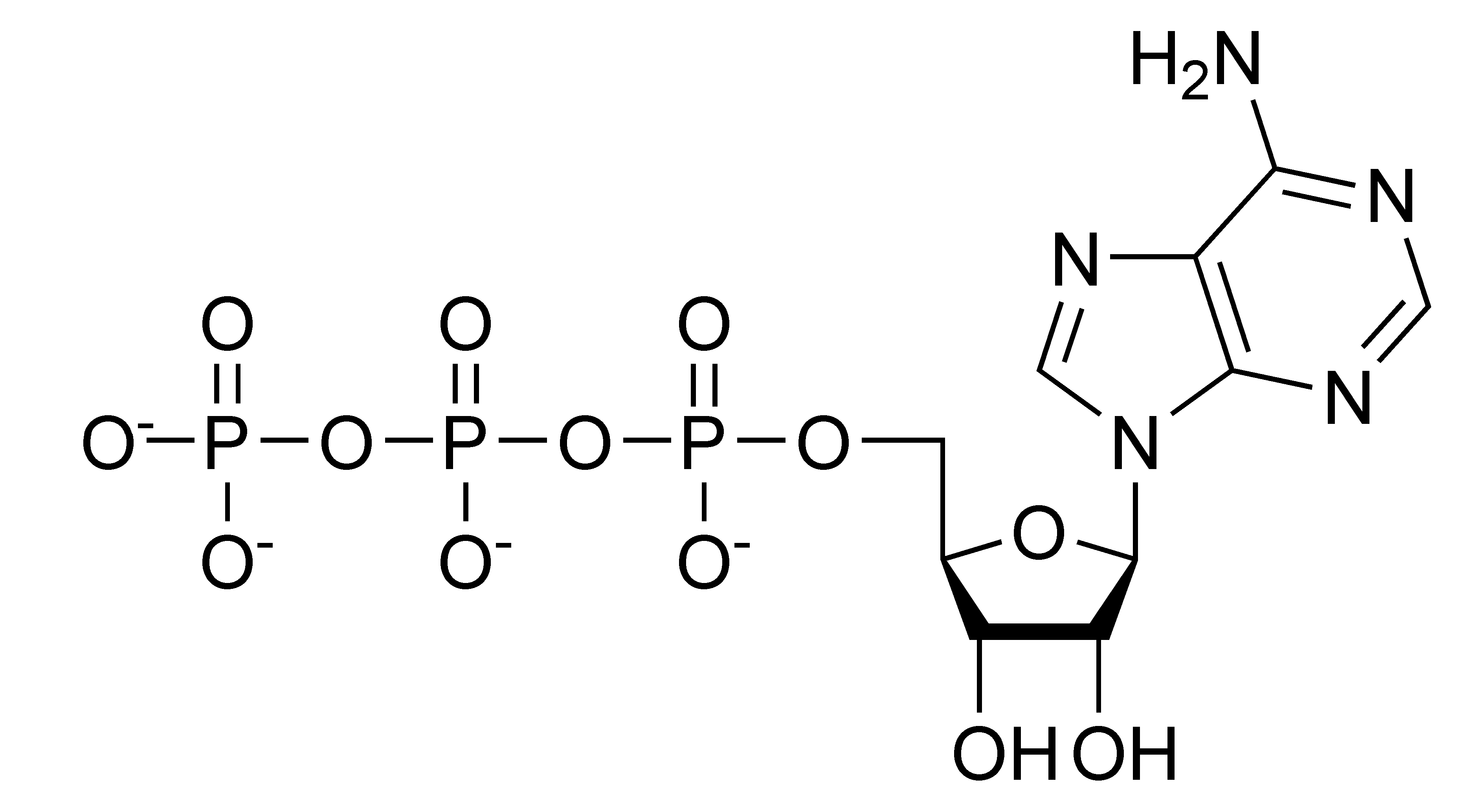
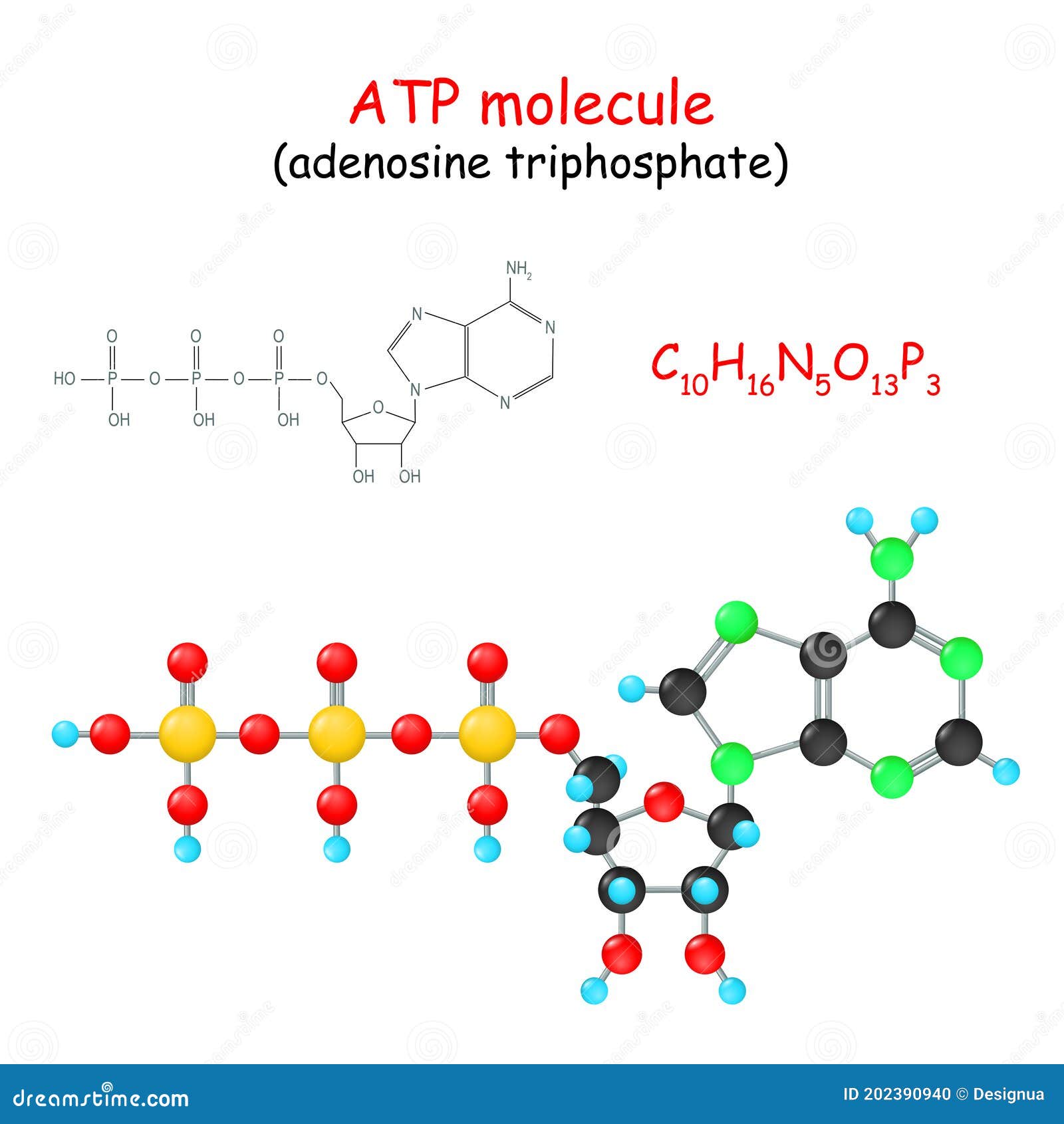
It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. Adenine ribose three phosphate groups here is. To harness the energy within the bonds of atp, cells use a strategy called energy coupling. As with most atp hydrolysis cases, a phosphate from atp transfers onto another molecule. Web atp, or adenosine triphosphate, is the energy currency in biological systems. The structure of atp is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts:
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Definition and Synthesis
Energy is stored when atp is formed and released when it's broken down into adp (adenosine diphosphate) and a phosphate group. As with most atp hydrolysis cases, a phosphate from atp transfers onto another molecule. The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is released when they are broken by the addition of a.
FileATP chemical structure.png Wikipedia
Adenosine triphosphate, also known as atp, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. The net products of this process are two molecules of atp ( 4 atp produced − 2 atp used up) and two molecules of nadh. Atp molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Web.
Atp Molecule Labeled, Atp Synthase Structure Function And Inhibition, 5
Web explore the fascinating process of atp hydrolysis! This molecule is composed of three parts: Web image of the atp cycle. Web scientists call this process of a phosphate group binding to a molecule phosphorylation. Web the body is a complex organism, and as such, it takes energy to maintain proper functioning. Adenine ribose three.
What is Adenosine Triphosphate? Definition, Function & Structure
The bonds between phosphate molecules are. Web interactive animation of the structure of atp adenosine triphosphate ( atp) is a nucleotide [2] that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and. Web atp is an unstable molecule which hydrolyzes to adp and.
StructureofATP PhD Muscle
As with most atp hydrolysis cases, a phosphate from atp transfers onto another molecule. This molecule is composed of three parts: Web atp is a highly unstable molecule. Track the atoms in different colors if that helps. Atp is like a charged battery, while adp is like a dead battery. Explore how glucose oxidation contributes.
Explain How Energy Is Released From Atp Wasfa Blog
Discover how water interacts with atp molecules, triggering a release of energy as bonds break and electrons find a more comfortable state. Web 1 answer acquaintance nov 22, 2016 adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups. In a phosphorylated state, the na + /k + pump has more free energy and is triggered to undergo a.
ATP and Sources of Energy.pptx on emaze
Adenosine triphosphate (atp) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. Web interactive animation of the structure of atp adenosine triphosphate ( atp) is a nucleotide [2] that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and. Web.
ATP Molecule
Web explore the fascinating process of atp hydrolysis! Although it carries less energy than glucose, its structure is more complex. That there are essentially three parts to the atp molecule: It's made up of adenosine and three phosphate groups. Adenine ribose three phosphate groups here is. To harness the energy within the bonds of atp,.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Definition and Synthesis
Although it carries less energy than glucose, its structure is more complex. Web atp is a highly unstable molecule. Web unravel the mystery of atp production in cellular respiration. Breaking of the phosphoanhydride bond, breaking of the water, and formation of new bonds to form adp and inorganic phosphate. Adenosine triphosphate, also known as atp,.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule. Functions as neurotransmitter
Adenosine triphosphate, also known as atp, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. Web atp is an unstable molecule which hydrolyzes to adp and inorganic phosphate when it is in equilibrium with water. (adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work. Let’s take a closer look at a molecule.
Draw A Molecule Of Atp Web interactive animation of the structure of atp adenosine triphosphate ( atp) is a nucleotide [2] that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and. The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is released when they are broken by the addition of a water molecule (a procedure known as hydrolysis). Web the most important donor of phosphate groups in the cell is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate, commonly known by its abbreviation atp. Include what is and is not recycled. The energy released from the hydrolysis of atp into adp + p i is used to perform cellular work.
Include What Is And Is Not Recycled.
As with most atp hydrolysis cases, a phosphate from atp transfers onto another molecule. In a phosphorylated state, the na + /k + pump has more free energy and is triggered to undergo a conformational change. Pgal releases electrons and hydrogen ions to the electron carrier molecule nadp+. Web unravel the mystery of atp production in cellular respiration.
Web Image Of The Atp Cycle.
That there are essentially three parts to the atp molecule: The structure of atp is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate. Let’s take a closer look at a molecule of atp, shown in the figure \(\pageindex{2}\). The net products of this process are two molecules of atp ( 4 atp produced − 2 atp used up) and two molecules of nadh.
Learn More About The Structure And Function Of Atp In This Article.
Adenine ribose three phosphate groups here is. Web interactive animation of the structure of atp adenosine triphosphate ( atp) is a nucleotide [2] that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and. Although it carries less energy than glucose, its structure is more complex. The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is released when they are broken by the addition of a water molecule (a procedure known as hydrolysis).
Adenosine Triphosphate (Atp) Is The Source Of Energy For Use And Storage At The Cellular Level.
Unless quickly used to perform work, atp spontaneously dissociates into adp + p i , and the free energy released during this process is lost as heat. Atp captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Web adenosine triphosphate (atp) is comprised of the molecule adenosine bound to three phosphate groups. Also notable, atp stands for adenosine triphosphate.



/adenosine-triphosphate-molecule-545861163-574f18965f9b582060dd2b4d.jpg)