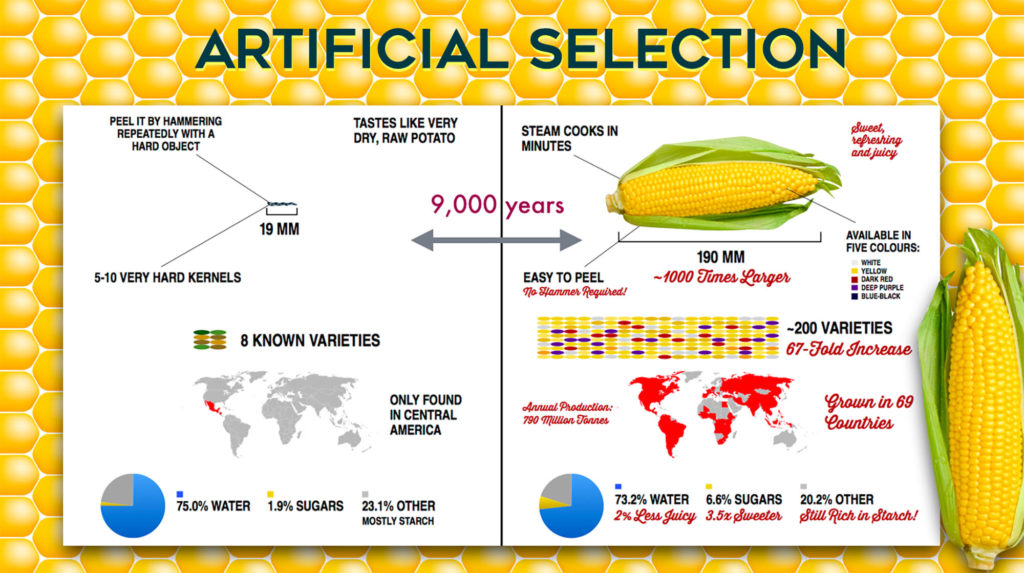
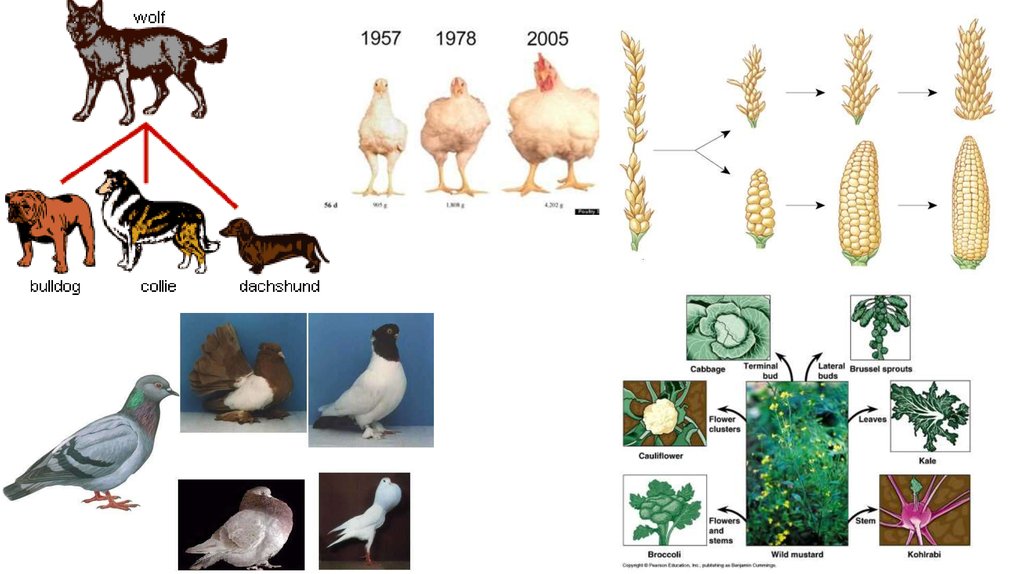
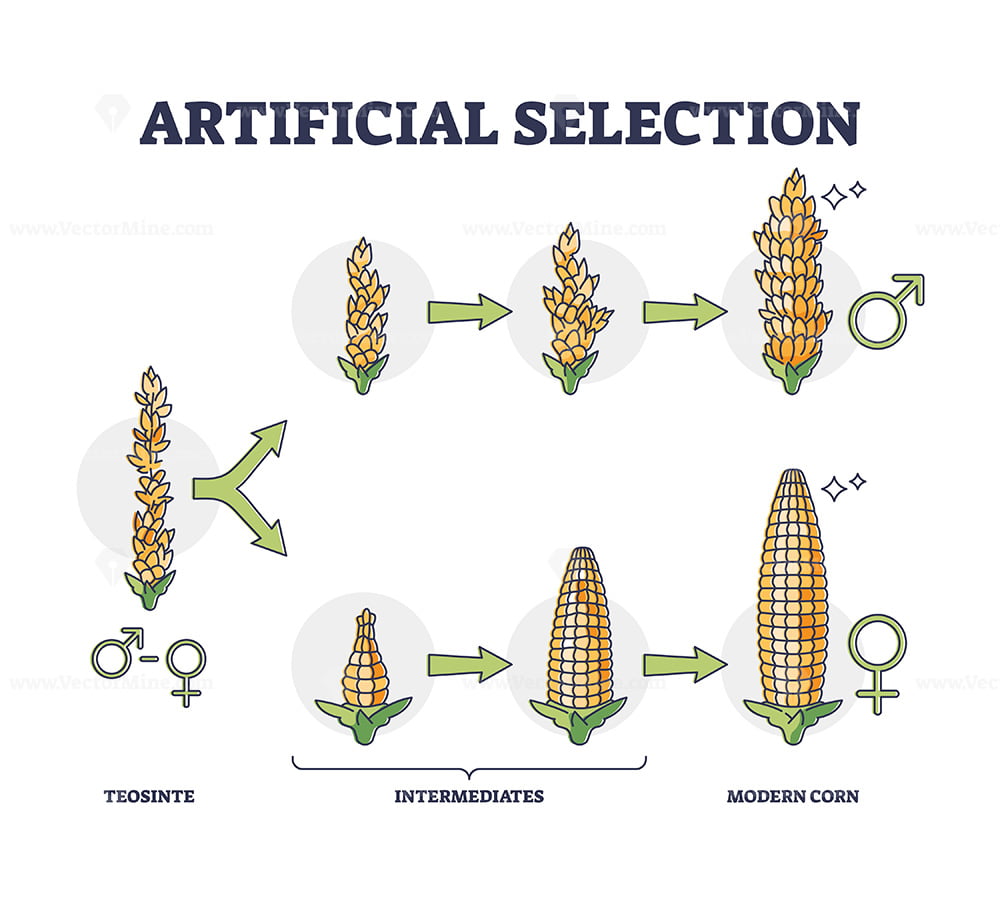
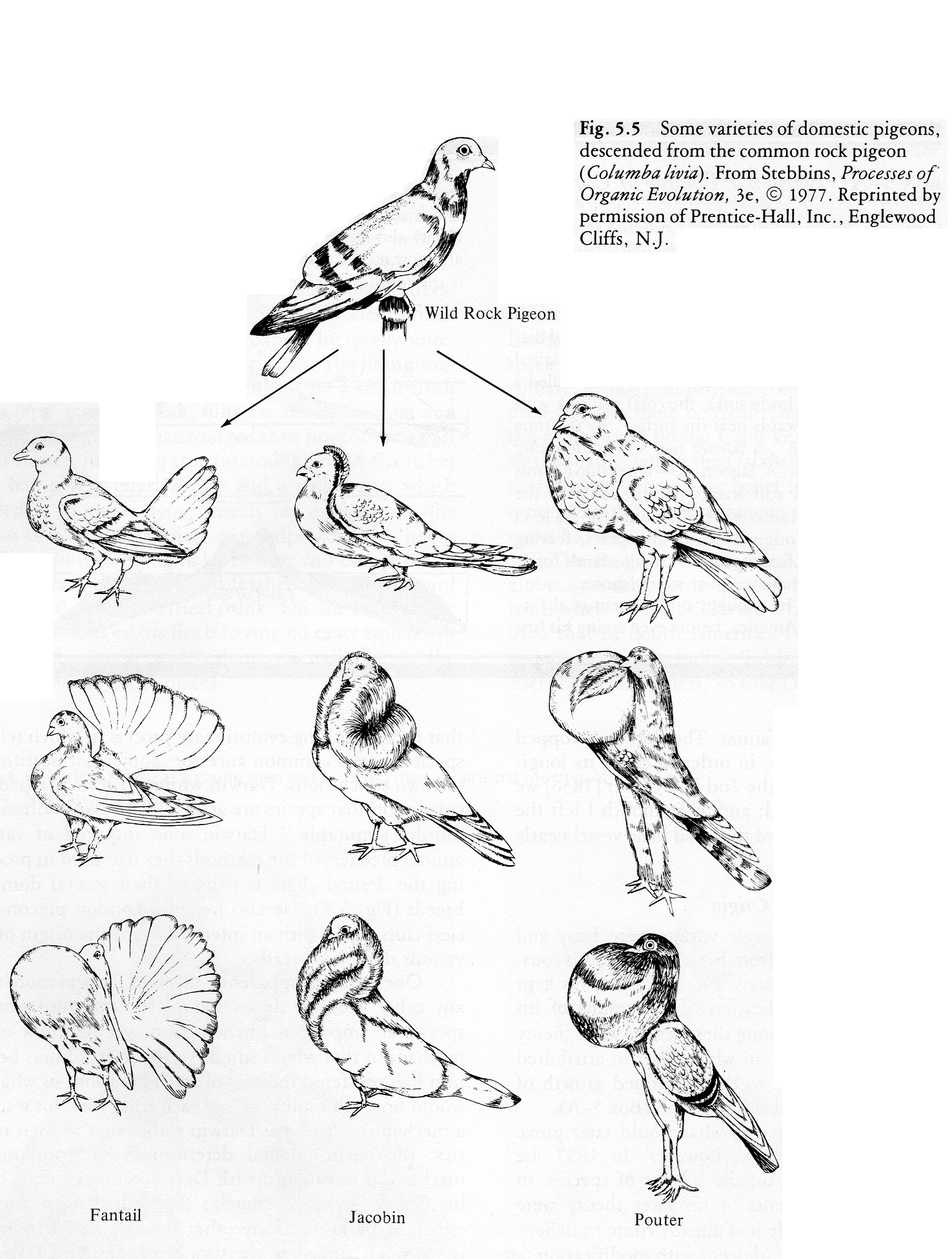
Artificial Selection Drawing
Artificial Selection Drawing - Web artificial selection (also known as selective breeding) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together. • discuss the differences and similarities between artificial and natural selection. Charles darwin introduced the term artificial selection in his book ‘on the origin of species (1859). Web artificial selection provides a model that helps us understand natural selection. Web the analogy, then, between artificial selection and natural selection includes mapping the principle of divergence in artificial selection to the principle of divergence in nature.
Web • explain the mechanism of selection and how selective breeding gives rise to complex features. Charles darwin introduced the term artificial selection in his book ‘on the origin of species (1859). Darwin artificial selection happened at hms beagle when he. • communicate results of experimental studies to a community of peers. Web artificial selection or selective breeding describes the human selection of breeding pairs to produce favorable offspring. 60 to 100 minutes grouping: During artificial selection, breeders use selective mating to promote traits that are desirable to humans.
Artificial Selection Nature Journals
This analogy is quite direct, except for a. Artificial selection aims to increase the productive or esthetic value of an organism to our advantage. Artificial selection accelerates change and shapes the. The process also applies to farm animals and crops, with humans selecting for desirable characteristics. Web artificial selection also remains a useful tool for.
Artificial selection online presentation
Web introduction artificial selection is distinct from natural selection in that it describes selection applied by humans in order to produce genetic change. Web artificial selection, also called selective breeding”, is where humans select for desirable traits in agricultural products or animals, rather than leaving the species to evolve and change gradually without human interference,.
Artificial Selection Plants Concept. Breeding New Varieties.
Web artificial selection is also known as selective breeding. Web artificial selection also remains a useful tool for illustrating key principles in evolutionary biology, especially since most people are familiar with many of the species that have been domesticated and with the general concept of selective breeding. In the process, a basic overview. Describe what.
Artificial selection with selective breeding for vegetables outline
60 to 100 minutes grouping: The process also applies to farm animals and crops, with humans selecting for desirable characteristics. Try an art generator now! Artificial selection aims to increase the productive or esthetic value of an organism to our advantage. Two to four teacher background: Darwin artificial selection happened at hms beagle when he..
Selection
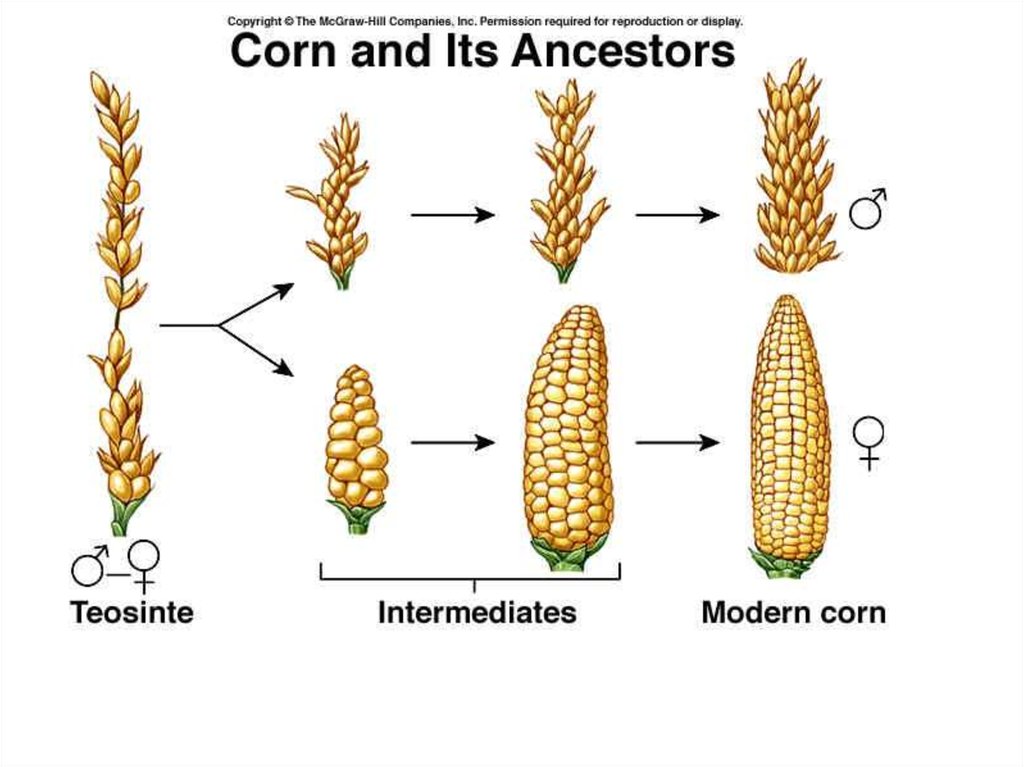
As shown below, farmers have cultivated many crops from wild mustard by artificially selecting for certain attributes. Selective breeding allows producers to select and breed parent organisms with desired traits to produce. Web artificial selection is also known as selective breeding. Web selective breeding (also known as artificial selection) is a technique still extensively used.
11 Biology Artificial Selection
This analogy is quite direct, except for a. Web artificial selection provides a model that helps us understand natural selection. Web selective breeding (also known as artificial selection) is a technique still extensively used by crop and livestock producers today. Artificial selection works the same way as natural selection, except that with natural selection it.
Evolution Artificial Selection online presentation
Web artificial selection is also known as selective breeding. Describe what you want to see random three men in spacesuits tending to the flowers in a geodesic dome of atmosphere on the moon. Web the analogy, then, between artificial selection and natural selection includes mapping the principle of divergence in artificial selection to the principle.
What Is Artificial Selection Adr Alpujarra
This analogy is quite direct, except for a. Another term for artificial selection is selective breeding. Bringing evolution closer to students’ everyday lives, such as with cases of domestication or diseases that we suffer from today, is an effective way to promote their interest in, and ultimately to help them. Web selective breeding (also known.
AN EXAMPLE OF ARTIFICIAL SELECTION FIGURE 1.10 Evolution of Wild
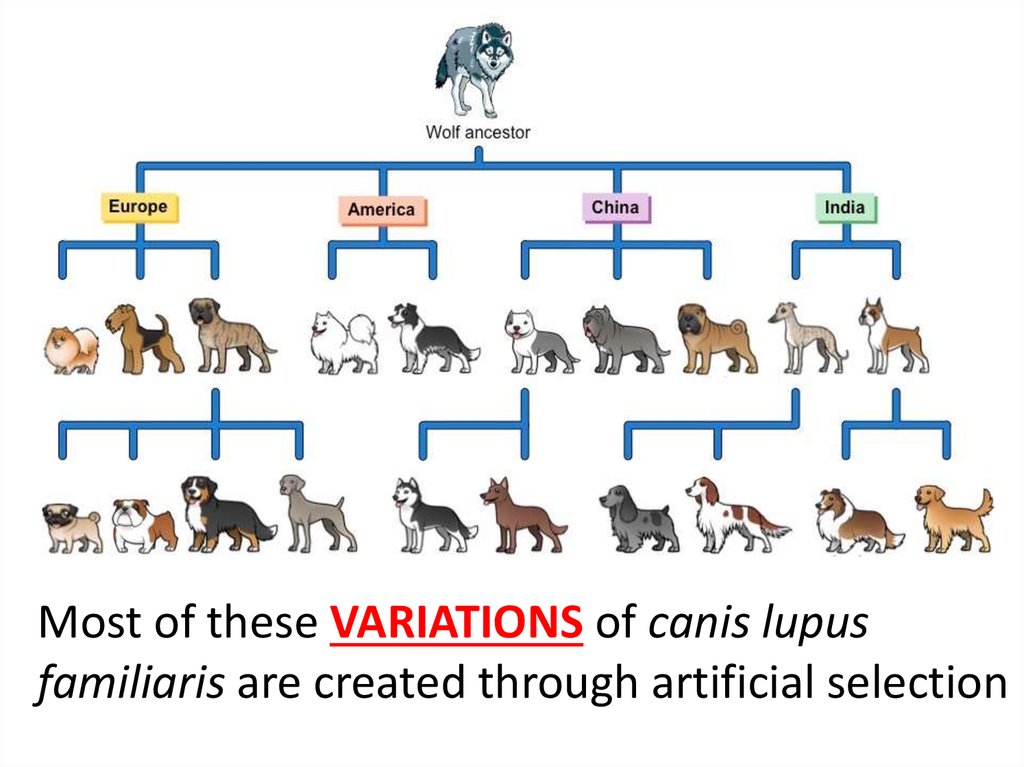
Dogs belong to a single species, canis familiaris, but that species is comprised of about 400 different. Selective breeding allows producers to select and breed parent organisms with desired traits to produce. • develop and test a hypothesis, using data to draw conclusions. Web the analogy, then, between artificial selection and natural selection includes mapping.
artificial_selection.html 22_10ArtifSelection.jpg
Web in particular, the present article reviews ten lessons about evolution that can be drawn from the modern understanding of domestication and artificial selection. Describe what you want to see random three men in spacesuits tending to the flowers in a geodesic dome of atmosphere on the moon. Web humans use artificial selection to develop.
Artificial Selection Drawing Artificial selection works the same way as natural selection, except that with natural selection it is nature, not human interference, that makes these decisions. When artificial selection is imposed, the trait or traits being selected are known, whereas with natural selection they have to be inferred. All crop plant varieties, types of livestock, and dog breeds are the result of artificial selection. Artificial selection accelerates change and shapes the. Darwin artificial selection happened at hms beagle when he.
Web Artificial Selection Is Also Known As Selective Breeding.
This analogy is quite direct, except for a. As shown below, farmers have cultivated many crops from wild mustard by artificially selecting for certain attributes. Web this process is called artificial selection because people (instead of nature) select which organisms get to reproduce. Web humans influenced breeding, selecting traits related to behavior and function.
Web The Analogy, Then, Between Artificial Selection And Natural Selection Includes Mapping The Principle Of Divergence In Artificial Selection To The Principle Of Divergence In Nature.
Web artificial selection or selective breeding describes the human selection of breeding pairs to produce favorable offspring. When artificial selection is imposed, the trait or traits being selected are known, whereas with natural selection they have to be inferred. Web artificial selection also remains a useful tool for illustrating key principles in evolutionary biology, especially since most people are familiar with many of the species that have been domesticated and with the general concept of selective breeding. Web we use artificial selection to help students understand natural selection, as darwin himself did by making an analogy between the two.
Pdf | On Jun 7, 2020, Bhumika And Others Published Artificial Selection | Find, Read And Cite All The Research You Need On Researchgate.
In this click & learn, students learn the genetic mechanisms of artificial selection and the similarities with the mechanisms of natural. Web selective breeding (also known as artificial selection) is a technique still extensively used by crop and livestock producers today. Artificial selection works the same way as natural selection, except that with natural selection it is nature, not human interference, that makes these decisions. Selective breeding allows producers to select and breed parent organisms with desired traits to produce.
• Discuss The Differences And Similarities Between Artificial And Natural Selection.
Web artificial selection, also called selective breeding”, is where humans select for desirable traits in agricultural products or animals, rather than leaving the species to evolve and change gradually without human interference, like in natural selection. Web artificial selection (also known as selective breeding) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together. A fancier’s unfulfilled desire for a certain extreme is analogous to an unoccupied place in the polity of nature. Darwin artificial selection happened at hms beagle when he.